circles#
Shapes made up of circles.
- class data_morph.shapes.circles.Bullseye(dataset: Dataset)[source]#
Bases:
RingsClass representing a bullseye shape comprising two concentric circles.
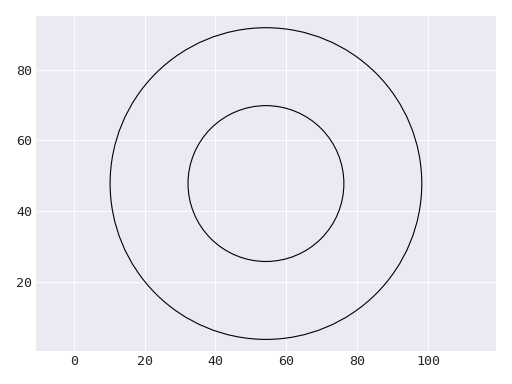
This shape is generated using the panda dataset.#
See also
CircleThe individual rings are represented as circles.
- distance(x: Number, y: Number) float#
Calculate the minimum absolute distance between any of this shape’s circles’ edges and a point (x, y).
- Parameters:
x (numbers.Number) – Coordinates of a point in 2D space.
y (numbers.Number) – Coordinates of a point in 2D space.
- Returns:
The minimum absolute distance between any of this shape’s circles’ edges and the point (x, y).
- Return type:
- name: str | None = None#
The display name for the shape, if the lowercased class name is not desired.
- plot(ax: Axes | None = None) Axes#
Plot the shape.
- Parameters:
ax (matplotlib.axes.Axes, optional) – An optional
Axesobject to plot on.- Returns:
The
Axesobject containing the plot.- Return type:
- class data_morph.shapes.circles.Circle(dataset: Dataset, radius: Number | None = None)[source]#
Bases:
ShapeClass representing a hollow circle.
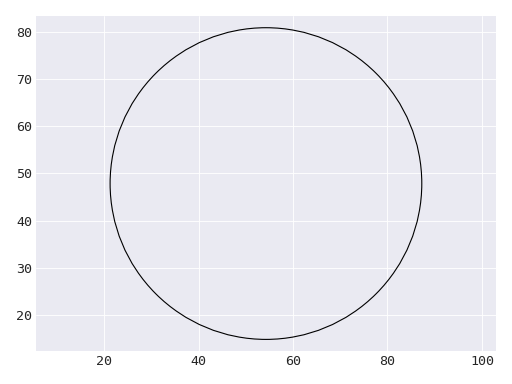
This shape is generated using the panda dataset.#
- Parameters:
dataset (Dataset) – The starting dataset to morph into other shapes.
radius (numbers.Number, optional) – The radius of the circle.
- distance(x: Number, y: Number) float[source]#
Calculate the absolute distance between this circle’s edge and a point (x, y).
- Parameters:
x (numbers.Number) – Coordinates of a point in 2D space.
y (numbers.Number) – Coordinates of a point in 2D space.
- Returns:
The absolute distance between this circle’s edge and the point (x, y).
- Return type:
- name: str | None = None#
The display name for the shape, if the lowercased class name is not desired.
- plot(ax: Axes | None = None) Axes[source]#
Plot the shape.
- Parameters:
ax (matplotlib.axes.Axes, optional) – An optional
Axesobject to plot on.- Returns:
The
Axesobject containing the plot.- Return type:
- radius: Number#
The radius of the circle.
- class data_morph.shapes.circles.Rings(dataset: Dataset)[source]#
Bases:
ShapeClass representing rings comprising three concentric circles.
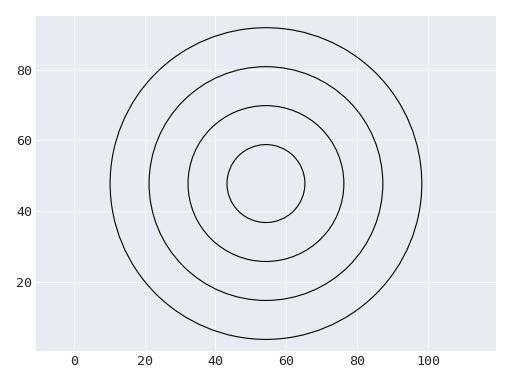
This shape is generated using the panda dataset.#
- Parameters:
dataset (Dataset) – The starting dataset to morph into other shapes.
See also
CircleThe individual rings are represented as circles.
- distance(x: Number, y: Number) float[source]#
Calculate the minimum absolute distance between any of this shape’s circles’ edges and a point (x, y).
- Parameters:
x (numbers.Number) – Coordinates of a point in 2D space.
y (numbers.Number) – Coordinates of a point in 2D space.
- Returns:
The minimum absolute distance between any of this shape’s circles’ edges and the point (x, y).
- Return type:
- name: str | None = None#
The display name for the shape, if the lowercased class name is not desired.
Modules
